What liver doctors will not tell you: Testing positive for Hepatitis virus does not necessarily mean you have viral hepatitis!

Hepatitis viruses are the most common cause of hepatitis, or inflammation of the liver. There are 5 main types of hepatitis viruses including types A, B, C, D, and E. Among these 5 types of viral hepatitis, hepatitis B and hepatitis C are the most common [1] Although there are some differences between HBV and HCV, there is one thing in common; both can cause severe damage to liver cells and lead to hepatitis. [2]
The public often have the following misconceptions regarding hepatitis viruses and viral hepatitis. Firstly, most people think that if hepatitis virus is present in their body, their liver would be attacked and thus they would have liver injury. However, this is not true. There are cases where the patient tests positive for hepatitis virus, yet their liver does not have inflammation.
Secondly, people logically believe that viral count is directly proportional to the degree of liver damage. This also, is not true. [3] In short, the relationship between hepatitis virus and liver damage can be summarized into 4 points:
- Testing positive for Hepatitis virus [does not equal] liver damage or hepatitis (liver inflammation).
- Testing negative for Hepatitis virus [does not equal] no liver damage. (As liver can be harmed by other substances such as alcohol, fat and drugs)
- A high viral count [does not equal] severe liver damage.
- A low viral count [does not equal] little liver damage.
Although chronic viral hepatitis is caused by hepatitis virus, there are other factors that affect the degree of damage and health status of the liver. These factors include our immune system, the recovery rate of liver cells, our diet and habits, fat contained in the liver, and the use of drugs, etc. Therefore, the most important figure to hepatitis patients or hepatitis virus carriers is not the viral load, but rather the ALT level. [4] The only way to ensure liver health is to maintain a normal ALT level! As mentioned in another article, only normal ALT level [equals] a healthy liver!
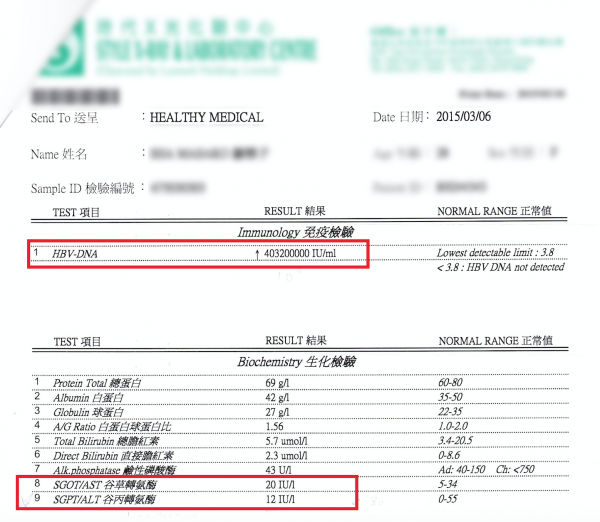
Below shows a blood test report of a hepatitis B carrier who has a high viral load, but liver function remains normal. This patient uses YHK liver therapy to enhance and protect the liver from virus attacks.
- Hepatitis- WHO. http://who.int/topics/hepatitis/en/ (Accessed: 2016-02-01)
- Differences between Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/Resources/Professionals/PDFs/ABCTable.pdf (Accessed: 2016-02-01)
- High Viral Count does not equal to liver damage http://www.zhangclinicnyc.com/hcv/articles/c5_vload.htm (Accessed: 2016-02-01)
- What is ALT level? https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003473.htm (Accessed: 2016-02-01)
- * All research and clinical data should be used as reference purposes only, results may vary.