Types of Liver Enzymes – How much do you know about them?
The liver is one of the five vital organs in the human body that are essential for survival, without which many of our bodily functions cannot take place. And in liver cells, various liver enzymes play an important role in completing different tasks on a daily basis. They are namely ALT, AST, ALP, and GGT.
Types of liver enzymes
|
Liver enzymes |
Where they are found |
Function |
Significance in liver blood test |
Normal range in a healthy individual (U/L - units per litre)* |
|
AST (Aspartate Transaminase) |
Found in various organs like liver, kidneys, heart, skeletal muscles, and brain |
Catalyses a type of amino acids which can then be used for energy production |
Not a very specific indicator of liver injuries because of its presence in many other organs |
5 to 40 U/L |
|
ALT (Alanine Transaminase) |
Largely concentrated in the liver and some in kidneys |
Converts amino acids for the process of cellular energy production |
A reliable indicator of liver damage |
7 to 56 U/L |
|
ALP (Alkaline Phosphtatase) |
Found mostly in the bile ducts of the liver and in bone |
Helps break down protein |
A helpful indicator to identify problems with the liver and gallbladder |
45 to 115 U/L |
|
GGT (Gamma-glutamyl transferase) |
Mostly found in the liver, however it is also present in the gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, and kidneys |
Transfers amino acids across cell membranes |
A reliable indicator for liver disease, especially on alcohol use |
9 to 48 U/L |
*Please note that the normal range listed here is only a rough guideline, as it varies among laboratories and countries.
Causes of elevated enzymes
Since the four enzymes have different functions in the liver, each elevated enzyme signifies different underlying causes.
AST/ALT ratio
AST/ALT ratio can provide insights to the patterns of liver diseases. In a study conducted by Pelagia Research Libary that compares levels of ALT, AST, ALP, and GGT in patients of various liver injuries, the following AST/ALT ratio was found.
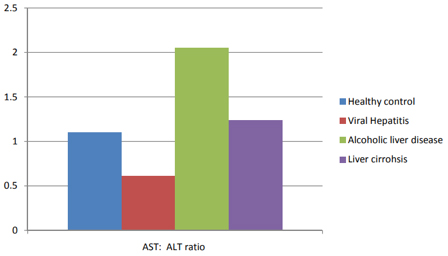
Generally speaking, healthy individuals would have an AST/ALT ratio of around 1. Any ratio higher than 2 suggests alcoholic liver disease. On the contrary, viral hepatitis patients would have an AST/ALT ratio of less than 1.0. As for non-alcoholic liver disease, patients would have an AST/ALT ratio of 2.0 or higher.
ALP
There are various reasons to account for an elevated ALP. In terms of liver-related causes, biliary obstruction, hepatic tumour, and viral hepatitis are common.
GGT
An increased level of GGT suggests hepatocellular injury, which is the most common type of primary liver cancer. Alcohol ingestion also attributes to GGT elevation.
Mildly elevated enzymes – What to do?
Among all the patients with elevated enzymes, not all show significant increases. When it comes to mildly elevated enzymes, it refers to having less than 5 times of the upper limit of normal levels. According to a study done by American Family Physician that focuses on the causes and evaluation of mildly elevated enzymes in asymptomatic patients, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common cause, with other causes being alcoholic liver disease, medication-associated liver injury, and viral hepatitis. And unsurprisingly, alcohol was found to be the cause of mildly elevated enzymes in 10% of 256 asymptomatic patients in a study conducted on the general Swedish population.
If patients are found to have mildly elevated enzymes, a physical examination and repeat testing in 2 to 4 weeks are recommended. Common causes such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease should be ruled out, followed by observing the lifestyle and considering less common causes. If none of this helps, liver biopsy should be considered.
While mild enzyme elevations might not always have serious underlying causes, it is always a good measure to prevent liver enzyme levels from going up further, this can be achieved by scientifically- proven liver therapy. Like treatments to many other diseases, prevention is always better than cure.
Contact our support team to find out more about liver protection.
- Pelagia Research Libary, https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/5255/4dac75e087ca4f69e0edbdf08269061ebbff.pdf (Access: 2018-05-18)
- Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/gamma-glutamyl-transpeptidase#outlook (Access: 2018-05-18)
- Lab Tests Online, https://labtestsonline.org/tests/alanine-aminotransferase-alt (Access: 2018-05-18)
- American Family Physician, https://www.aafp.org/afp/2011/1101/p1003.html (Access: 2018-05-18)
- Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, https://www.mdedge.com/ccjm/article/95275/gastroenterology/when-and-how-evaluate-mildly-elevated-liver-enzymes-apparently (Access: 2018-05-18)
- Medicine Net, https://www.medicinenet.com/liver_blood_tests/article.htm#what_blood_tests_are_done_to_detect_liver_function_continued (Access: 2018-05-18)
- * All research and clinical data should be used as reference purposes only, results may vary.